Using and Pushing Docker Images With Bazel
We’re Earthly. We make building software simpler and therefore faster. This article is about when to reach for Bazel. If you are looking for a simpler approach to building monorepos then check us out.
Bazel is an open source build and test tool that helps you automate your software tasks using a defined set of rules from an abstract, human-readable source code. Initially developed by Google, Bazel is a versatile tool that supports multiple programming languages and software environments.
Using Docker images with Bazel allows for even more scalability than what Docker or Bazel could offer you alone. This is because different parts of the project can be run in lightweight, portable, and isolated containers and can be executed in parallel across multiple machines or clusters. Moreover, Bazel offers easy compatibility with rules_docker, which are premade rules for carrying out Docker tasks. What’s great about these rules is that you don’t need to write Docker commands for pulling, building, or pushing images as the rules will take care of all these, thereby simplifying the development process. This can be particularly useful for large-scale projects that require the use of multiple Docker images, as it streamlines the process of building and deploying those images
As an experienced developer, in this article, you’ll learn more about how Docker and Bazel work together and how to use and push Docker images as part of the Bazel build process.
Docker and Bazel
Bazel works with Docker by creating and testing applications inside Docker containers using Bazel’s rules. A rule in Bazel specifies a set of operations that Bazel carries out on a set of inputs to generate a collection of outputs, which can then be referenced and used in other downstream actions and providers. Bazel’s predefined language-specific rules come with the option to create your own custom rules.
As previously mentioned, Bazel’s rules_docker allows you to download base images, enhance them with build artifacts and assets, and publish or push the images to a repository. Additionally, it offers the ability to perform commands inside Docker containers and install packages.
Moreover, Bazel provides an easy-to-use interface for building and testing projects with Docker, enabling you to easily create and manage consistent and isolated container environments for your projects.
Using Docker With Bazel

In this tutorial, you’re going to use Docker with Bazel by pulling a Docker image, using that image as a base to create another image, and finally pushing the created image to Docker Hub, all within a Bazel workflow.
Before you begin, you’ll need the following:
- Bazel: This is available for installation across Linux, macOS, and Windows systems. You can follow the instructions in their installation guide to download the version of Bazel that you need.
Please note: Bazel’s rules_docker is currently not supported on Windows.
- Docker: You’ll need active Docker credentials to pull and push images to Docker Hub. You can define your custom Docker configuration in Bazel or run the following command in your terminal to grant access to your subsequent commands:
docker login Sample Project Creation
Because Bazel projects have a specific structure that needs to be followed, before commencing development, it’s necessary to create a workspace for your project. A workspace is a directory that stores the source files for your project as well as the build outputs produced by Bazel. Within this directory, you’ll have a WORKSPACE file and one or more BUILD files.
The WORKSPACE file should be located at the root of your project’s directory tree. It’s responsible for determining whether a given directory and its contents constitute a Bazel workspace. It’s also used to define dependencies and requirements for the project space. A project with interdependent files will share one WORKSPACE file.
A BUILD file contains the instructions given to Bazel to execute. It should contain at least one set of instructions or rules and can encompass multiple languages and instruction sets. In this file, you’ll declare your chosen targets and the appropriate outputs, such as executable binaries or libraries for Bazel. A directory within the workspace that contains a BUILD file is called a package.
Your Bazel structure can look like this with multiple workspaces and different packages defined within them. Workspaces and the packages within them can be referenced anywhere within your main directory:
main_directory
└── bazel_files
├──workspace1
│ ├── package
│ │ ├── BUILD
│ │ └── executable.cc
│ └── WORKSPACE
├──workspace2
│ ├── package
│ │ ├── BUILD
│ │ ├── executable1.cc
│ │ ├── executable2.cc
│ │ └── executable3.h
│ └── WORKSPACE
└──workspace3
├── package1
│ ├── BUILD
│ ├── executable1.cc
│ ├── executable2.cc
│ └── executable3.h
├── package2
│ ├── BUILD
│ ├── executable1.cc
│ └── executable2.h
└── WORKSPACE
To create a sample project, you need to create a directory on your terminal and then create a WORKSPACE file within that directory:
mkdir bazel_test
cd bazel_test
touch WORKSPACEThe contents of your WORKSPACE file are dependent on your project and the rules you declare. Insert the following code in your WORKSPACE file:
workspace(
# Naming your workspace can help you reference it elsewhere, \
in other workspaces or projects
name = "bazel_docker_test",
)
## Download the Bazel repository (rules_docker) as a compressed archive \
file, decompresses it, and makes its targets or functions available \
for binding.
load("@bazel_tools//tools/build_defs/repo:http.bzl", "http_archive")
http_archive(
name = "io_bazel_rules_docker",
sha256 = "b1e80761a8a8243d03ebca8845e9cc1ba6c82ce7c5179ce2b295cd36f7e394bf",
urls = ["https://github.com/bazelbuild/rules_docker/releases/download/v0.25.0/rules_docker-v0.25.0.tar.gz"]
)
### Docker Setup: loading the archived repository as well as its dependencies
load("@io_bazel_rules_docker//repositories:repositories.bzl", \
container_repositories = "repositories")
container_repositories()
load("@io_bazel_rules_docker//repositories:deps.bzl", \
container_deps = "deps")
container_deps()
## loading a specific function from the rules_docker repository, \
the container_pull function
load(
"@io_bazel_rules_docker//container:container.bzl",
"container_pull"
)
container_pull(
name = "flask_base",
registry = "index.docker.io",
repository = "sootersaalu/flask_base",
tag = "v.0.1"
)
Here, you define your workspace, call the rules_docker repository and its dependents, and pull a Docker image from Docker Hub. The flask_base image that is called provides the dependencies for creating a flask application, installing Python and Flask in the created container.
Next, you need to create your BUILD file:
nano BUILDInsert the following code in your BUILD file to define the rules you’re using, their targets, and the outputs of Bazel’s execution process:
## Loading the needed functions from the rules_docker repository
load("@io_bazel_rules_docker//container:container.bzl", \
"container_image")
load("@io_bazel_rules_docker//container:container.bzl", \
"container_push")
# container_image packages a new docker image, new layers \
can be added to a base image using its parameters
container_image(
name = "my_app",
base = "@flask_base//image",
entrypoint = ["main.py"],
files = [
"main.py"
],
ports = ["5000"],
)
# container_push pushes a local image to a registry of your\
choice (Docker Hub, Google Registry, Gitlab registry or Github packages)
container_push(
name = "publish",
format = "Docker",
image = ":my_app",
registry = "index.docker.io",
repository = "{your_repository}/bazel_docker_test",
tag = "1",
)Please note: You should update
{your_repository}to your specific Docker repository.
With this, you’re building an image with the container_image function. This new image is created using the image you pulled within your WORKSPACE file as a base and then adds executable files and parameters for the Docker container. The image built can then be pushed using the container_push function to your Docker Hub repository.
You will need a main.py file for your image. This code file will contain the mechanics of the application you’re enclosing within your image. This is necessary for the application to operate correctly inside the Docker container:
nano main.pyAdd the following code to create a basic Flask application that functions as a simple calculator:
from flask import Flask
from random import randint
app = Flask(__name__)
def my_calculator(self, x, y): return x + y
@app.route('/')
def randomcal():
num1 = randint(0, 100)
num2 = randint(0, 100)
message = "{} + {} = {}!".format(num1, num2, \
my_calculator.add(num1, num2))
return message
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0')Bazel Execution
With your workspace set up, you can start utilizing Bazel commands to execute the instructions you declare and create the outcomes you want. To begin, you need to utilize the bazel build command. This loads all the packages in the dependency graph of your BUILD files, whether they are declared or not. After finding all the dependencies, Bazel verifies that they’re correct and then creates the build actions.
Run the following command in your terminal:
bazel build "//…"The "//…" parameter tells Bazel to build all the targets it finds in your directory:
Then run each of your targets to execute the instructions declared in your BUILD file:
bazel run :my_app
bazel run publishThis code creates an image in the terminal using your previously declared Docker image as a base, then pushes the created image to Docker Hub under the repository you defined in your BUILD file:
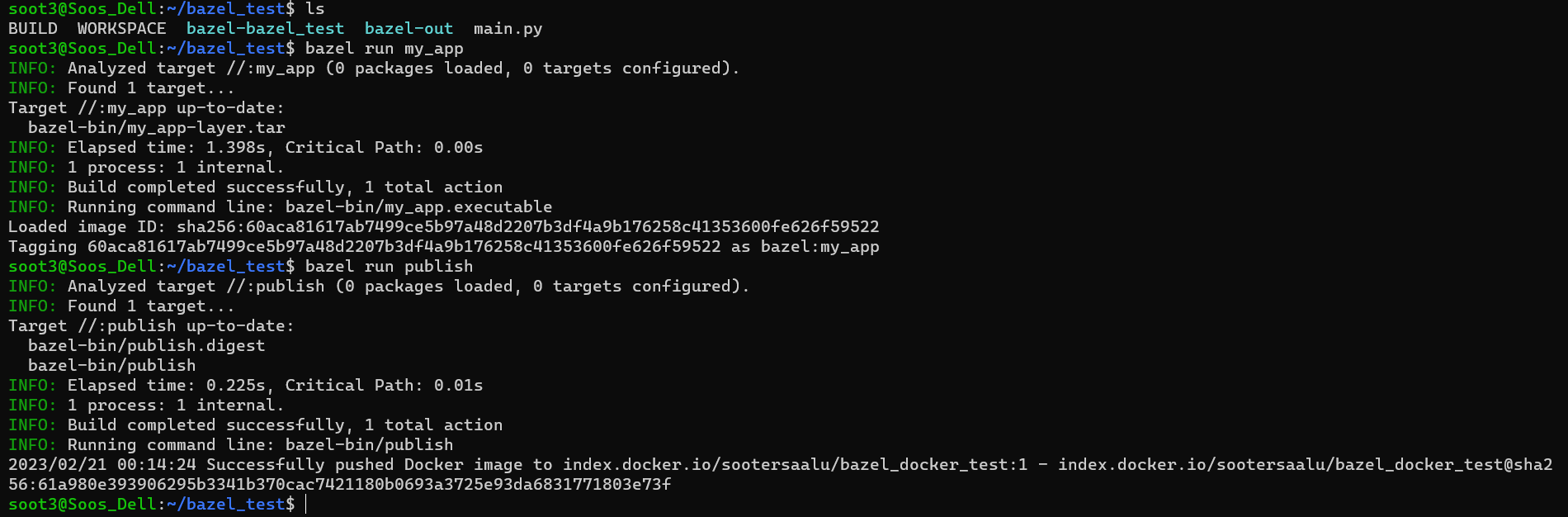
bazel run command resultsYou can find all the code for this tutorial in this GitHub repo.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Docker and Bazel can work together efficiently to optimize your development process. Bazel’s powerful rule-based structure simplifies the task of managing Docker images, testing software within Docker containers, and deploying applications. This rule-based system provides flexibility, extensibility, and reliability that few other build systems can match.
Yet, while Bazel is a fantastic tool for managing Docker images and containerizing software, it can also be complex and intricate. It may be overkill for smaller projects or for teams that aren’t familiar with its intricacies. That’s where Earthly comes into the picture.
Earthly offers a simpler approach to building monorepos and containerization, focusing on streamlining the build process, maintaining a minimal setup, and promoting the use of best practices. It aims to simplify the build system and make it accessible for more developers, offering a potentially lower learning curve compared to Bazel. Earthly can handle both small and large projects, offering you scalability without the additional complexity.
Remember, the ultimate goal is to choose a tool that not only suits your current needs but also has the capacity to grow with you and your project, all the while ensuring a simpler, faster, and more efficient software development process. Be it Bazel, Docker, Earthly, or any other tool, the choice should make your build process a breeze, not a hurdle.
Earthly makes CI/CD super simple
Fast, repeatable CI/CD with an instantly familiar syntax – like Dockerfile and Makefile had a baby.










