Introduction to Netlify Cloud Functions
We’re Earthly. We make software development simpler and faster using containerization. Want to improve your workflow when you’re working with Netlify Functions? Earthly can smooth out the build process. Check it out.
When building backend applications, we often have to add features that are not supported by the current stack or would slow down our applications. A possible workaround is to use cloud functions that help abstract away some of these tasks.
This tutorial will cover how to create Netlify Functions, then explain an example use case, and best practices for using Netlify Functions. We will also take a look at how Netlify Functions compare to AWS Lambda and why you might prefer one over the other.
What Are Serverless Cloud Functions?
Cloud functions are pieces of code that run in the cloud and are triggered by an event. They are written in a serverless language, like JavaScript, and are hosted and managed by a cloud provider, such as Netlify or AWS.
Cloud functions are used to respond to webhooks, process form submissions, and respond to API requests. Also used for authentication, authorization, and other security tasks. Image or video processing and manipulation, text generation, and more. Cloud functions provide an efficient way to offload processes from a main server, as they are triggered by an HTTP request and are managed by the cloud provider
What Are Netlify Functions?
Netlify functions are a serverless, cloud-based function as a service (FaaS) platform; they are to help developers build and deploy their applications quickly and easily.
Netlify functions are serverless functions built on top of AWS Lambda, designed to enable developers to quickly and easily deploy and manage code snippets. Functions can be written in JavaScript, Go, or TypeScript, and are triggered by an HTTP request. As mentioned, Netlify functions provide an efficient way to create powerful applications, offloading time-consuming tasks such as webhooks, form submissions, API requests, authentication, authorization, and more to the cloud.
Netlify cloud functions can be used for a variety of purposes, including creating serverless backends for applications, providing custom APIs for third-party apps, or even handling real-time data processing and analysis.
Types of Netlify Functions
In this article, we’ll take a look at the different types of Netlify functions, including background functions, trigger functions, and scheduled functions, and how they can be used to enhance your web development workflows.
Background Functions
Netlify’s Background Functions provide a serverless function option that can take up to 15 minutes to complete and does not need to be finished before a visitor can move on to the next step on your website. This type of function may be more suitable than synchronous functions for tasks such as batch processing, web scraping, and slower API workflow execution.
At the time of writing—this is still in beta—but I’ve been using it for months, and it is great!
Trigger Functions
Trigger functions are serverless functions that are triggered when a specific event occurs, such as when a webhook is sent or when a form submission is received. They are designed to respond to events and perform certain tasks, such as sending an email or updating a database, without the need for a traditional server.
Trigger functions are used to quickly and easily add functionality to your web applications without the need for a lot of setup or configuration.
Netlify’s Trigger Functions offer an efficient way to respond to HTTP requests, process form submissions, and respond to webhooks. They are easy to set up and configure, and can be written in JavaScript, Go, or TypeScript. Trigger functions are triggered by an HTTP request and can be used to quickly and easily add powerful functionality to your web applications.
Scheduled Functions
Netlify functions’ scheduled functions feature allows you to run functions on a regular and consistent basis, similar to a cron job. These functions can be used for a variety of tasks, though some are more suitable than others.
How Does Netlify Organize Its Functions?
Netlify organizes its cloud functions and files using a hierarchical structure. At the top level, there is a root directory that contains all the files and folders associated with the project. Each folder contains files and subfolders related to a specific function or feature.
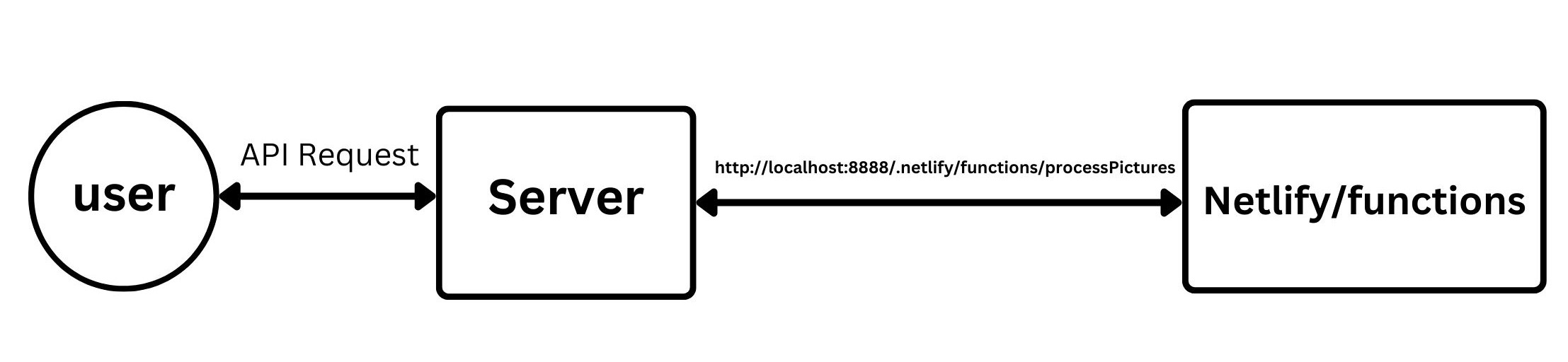
Let’s say you are building a website that allows users to upload pictures. You want to create a cloud function that will process the pictures that are uploaded by the users. The first step would be to create a folder named “functions” in your project directory. Inside this folder, you’ll create a file called processPictures.js which contains the code for the cloud function. The name of this file would be included in the HTTP request to access the function.
For example, if you want to access the cloud function to process the pictures uploaded by the user, the HTTP request would look like this, http://localhost:8888/.netlify/functions/processPictures. This would allow your cloud function to be accessed and used to process the pictures uploaded by the user.
How To Create Netlify Functions

To sum up: A Netlify function is simply a file that is triggered by an HTTP request. Let’s say you want to build a simple contact form for your website that stores subscribers to a firebase database. To read more on firebase and documentation.
You can create a Netlify Function that is triggered by an HTTP request and sends an email to firebase when the form is submitted. This lets you abstract the firebase credentials from being loaded on the Frontend and prevents malicious people from getting that info.
The code examples in the article can be found in this GitHub repo.
Step 1: Create a Netlify Function Project
Creating Netlify Functions is a fairly straightforward process. The first step is to create a Netlify Function project.
Run the following command in the project directory:
netlify init If you don’t have Netlify set up, you can install it using npm using the following command:
npm install netlify-cli -gThis will create the necessary files and folder structure for your Netlify Functions project. You will then need to create a netlify.toml file to define the configuration for your functions. Here you will specify the name of your function, the runtime, the entry point, and any environment variables that your function needs.
Here is a simple example:
[build]
functions = "netlify/functions/"
[context.dev.environment]
apiKey = "***********"
authDomain = "***********"
projectId = "***********"
storageBucket = "***********"
messagingSenderId = "***********"
appId = "***********"The toml file can be broken down into sections:
[build]
functions = "netlify/functions/"This code above tells Netlify to look for functions in the “netlify/functions/” directory. This allows Netlify to deploy and run serverless functions from that directory.
[context.dev.environment]
storageBucket = "***********"
apiKey = "***********"
authDomain = "***********"
projectId = "***********"
storageBucket = "***********"
messagingSenderId = "***********"
appId = "***********"For example, you might need to specify the firebase credentials for your service so that your function can store data in firebase. This can be done in the context.dev.environment.
Once you have your netlify.toml file set up, you can create your function.
Step 2: Create a Firebase Configuration File
In this step, we are creating a configuration file for our Firebase project. This file will contain the necessary credentials to authenticate the Firebase API, and will also export an object which we can use to save data to Firebase.
The code starts by requiring the Firebase package, which will provide the necessary methods to interact with the Firebase API. We then create an object called firebaseConfig, which contains the credentials necessary to authenticate the API. These credentials are typically stored as environment variables.
Once the configuration object is set up, we call initializeApp() from the Firebase package, and pass in the configuration object. This will create an instance of the Firebase app and store it in a variable.
Finally, we export the Firebase app so that it can be used elsewhere in our application. This will allow us to access the Firebase API and save data to our database.
//functions/subscriber.js
const firebase = require("firebase")
// Your web app's Firebase configuration
var firebaseConfig = {
apiKey: process.env.apiKey,
authDomain: process.env.authDomain,
projectId: process.env.projectId,
storageBucket: process.env.storageBucket,
messagingSenderId: process.env.messagingSenderId,
appId: process.env.appId
};
// Initialize Firebase
firebase.initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// export Firebase so it can be used elsewhere
const FireBase = firebase.initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
export default Firebase;Step 3: Create Your Function File
Next, you’ll need to create your function that would be able to perform our action. To do that create a JavaScript file and export a function called handler.
To do this, create a file called subscriber.js in the functions folder.
touch functions/subscriber.js//subscriber.js
const FireBase = require("../config.js")
exports.handler = async (event, context) => { /// handler
console.log('Sending the email');
try {
const {email} = JSON.parse(event.body);
const saveToFirebase = FireBase.firestore();
saveToFirebase.collection("subscribers").add({
email,
createdAt: new Date()
});
return { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify({ success:true }) };
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
return {
statusCode: 500,
body: JSON.stringify( { error: ' Failed fetching images ' } ),
};
}
};The handler function is very important, this is the function that is called by Netlify, very similar to the main function in python.
The code snippet above exports a function called handler which is an asynchronous function that takes in two parameters: event and context. The handler attempts to extract an email address. This email address is then used to create a FireBase document with the email address and the current date and save it to the FireBase database. Finally, the handler function returns a status code of 200 and a body of {success:true} to signify that the email has been sent.
If there is an error in the code, or in the request, the handler function will catch the error and return an error response with a status code of 500 and an error message. This error message will help to identify and debug any issues with the code or the request.
Once your function is written, you can deploy it to Netlify and it will be available to be triggered by an HTTP request.
Step 4: Test and Deploy Your Function
Running netlify dev in our terminal runs our function; we can access it using a post request at http://localhost:8888/.netlify/functions/subscriber:
POST http://localhost:8888/.netlify/functions/subscriber
{
"email" : "test@earthly.com"
}Other Use Cases
Here are some other applications where you can try using Netlify Functions:
- Performing automated tasks triggered by external events
- Generating dynamic responses to web requests
- Creating real-time applications with Websockets and serverless functions
- Sending SMS messages or emails with serverless functions
- Creating custom webhooks to trigger external events
- Handling file processing and uploads
- Processing payments with serverless functions
- Automating image manipulation and optimization
AWS Lambda vs. Netlify Functions
AWS Lambda and Netlify Functions are both serverless compute services that run code in response to events and automatically manage the underlying compute resources, both are designed to be easy to use, however, they have some key differences.
AWS Lambda is a fully managed service that takes care of all the operational and administrative complexities of deploying and managing your code. It is highly scalable and can be used to build applications of any size.
Netlify Functions are also serverless functions, but they are designed to be used in conjunction with Netlify’s hosting and deployment services. They are best for small-scale applications and are not as scalable as AWS Lambda. Additionally, Netlify functions require minimal setup and configuration.
With Netlify, you can deploy your functions with a single command, while with AWS Lambda, you need to set up an entire serverless infrastructure. Additionally, Netlify Cloud Functions are more cost-effective than AWS Lambda, as they are billed on a per-request basis, rather than a per-hour basis.
Conclusion
Netlify Functions offer a convenient way to include serverless functionality in your web projects, simplifying the process of creating small APIs or dynamic site elements. Now that you’re familiar with these Functions, delve deeper into Netlify’s documentation and tutorials to enhance your usage.
If you’re looking to streamline your build processes for serverless apps, you might want to give Earthly a shot. It’s an excellent tool that can help optimize your workflow.
Earthly makes CI/CD super simple
Fast, repeatable CI/CD with an instantly familiar syntax – like Dockerfile and Makefile had a baby.










